Download PDF
Interest Rate Increases on the Horizon
We are seeing it at the grocery store and the gas pump – prices are rising. The topic of inflation is receiving a lot of attention as observers wait to see how governments will act to address those rising prices. With central banks around the world either considering or already increasing interest rates in 2022 to combat inflation, we are reminded that the prolonged low interest rate environment that has prevailed in Canada for more than a decade is atypical in the context of long-term monetary policy and is unlikely to persist indefinitely. In January 2022, Bank of Canada Governor Tiff Macklem noted in an interview during the same week that, “the message is pretty clear. We’re on a rising path.” (1).
More recently, on March 2nd 2022, Bank of Canada’s target for the overnight lending rate (a key benchmark for lending rates in Canada) was raised to 0.50% from 0.25% (2), marking the first time rates have changed since the COVID-19 pandemic in early 2020. In an accompanying statement, the Bank of Canada noted the emergence of conflict in Ukraine has led to increased uncertainty in global markets and has also caused prices for oil and other commodities to rise sharply in recent weeks, which will increase inflationary pressure above what was initially anticipated in January 2022 (2).
As a source of alternative financing for Canadian farmers, and a manager of a diversified portfolio of Canadian farmland, Bonnefield is often asked what impact rising rates may have on farm operators and farmland values in Canada. We’ve provided some thoughts on this complex relationship in the following sections.
A Recent History of Inflation and Interest Rates in Canada
As of February 2022, the Canadian Consumer Price Index (“CPI”; index of all goods including gasoline) rose again to 5.7%, remaining above the Bank of Canada’s target normalized range of 1-3% reaching its highest level since August 1991 (3). Generally, prices begin to increase when the demand for goods and services outpaces the supply of those goods and services in the economy. Price inflation in turn reduces the purchasing power of individuals, which can have a significant impact on the overall standard of living.
When faced with increasing levels of price inflation, central banks have few policy options to cool price increases and to alleviate the financial strain caused by elevated prices for goods and services. A gradual increase in key lending rates, such as the Bank of Canada’s target overnight rate, can help to reduce spending, thus tempering the demand side of the equation and slowly reducing inflationary pressures. Despite a now-lengthy cycle of low rates and the continued effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, it is very apparent that increased interest rates are on the horizon. When asked about the timing of target rate hikes, Tiff Macklem responded to reporters in January 2022, “How far and how fast? Those are decisions we’ll take at each meeting, depending on economic developments, depending on our outlook for inflation, and what we judge is needed to bring inflation back to target.” (1)
Canadian Consumer Price Index (CPI) Monthly 12-Month Percentage Change Data (2016-2022)
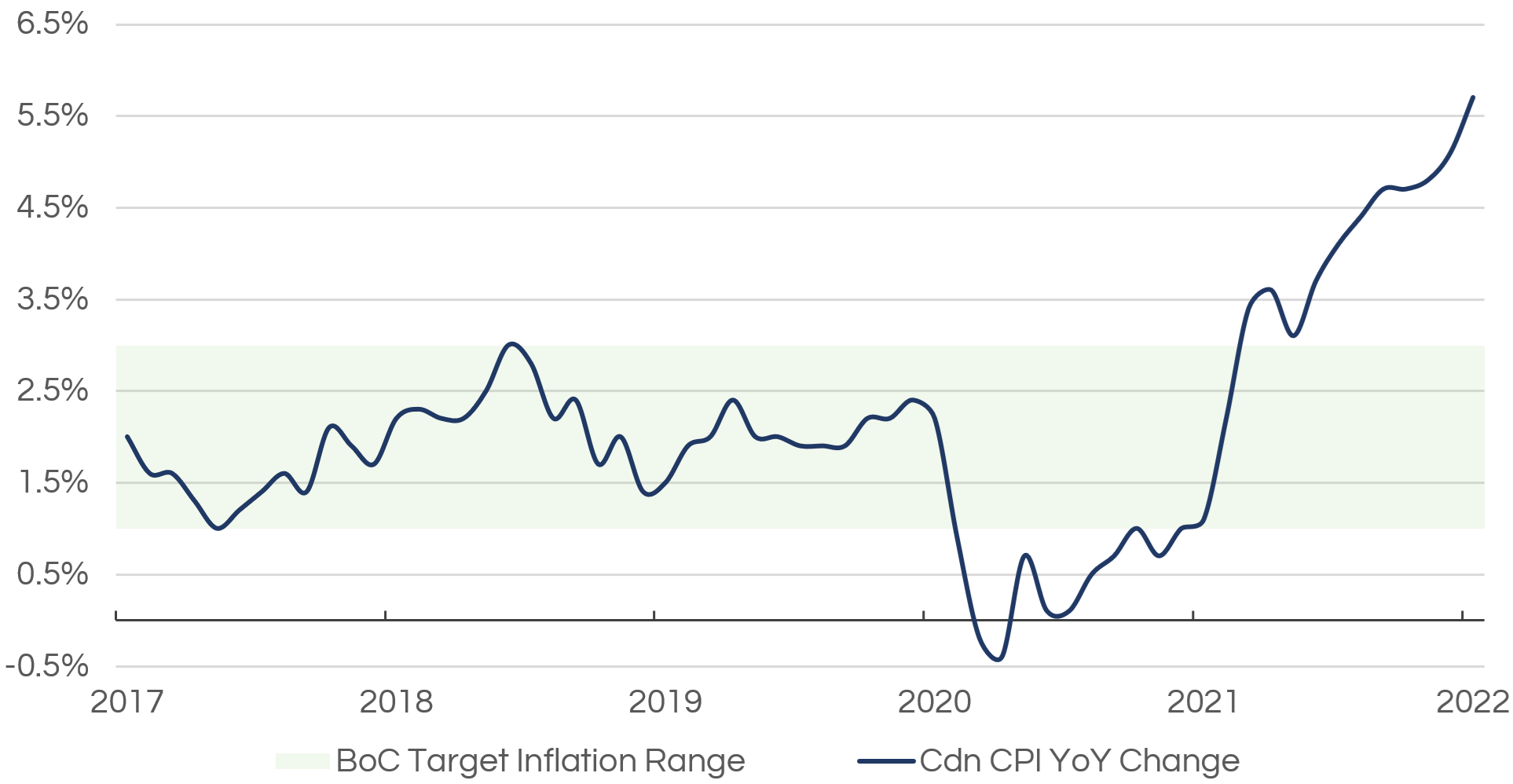
Source: Bank of Canada, Statistics Canada.
Interest Rates on Farm Balance Sheets
From a balance sheet perspective, while the principal amount of a loan is not directly affected by a change in borrowing costs, the total amount of capital that must be repaid to lenders over time increases when rates rise. In turn, this increases the overall financial riskiness of farmers’ balance sheets and leads operators to carefully consider whether certain expenditures and investments are necessary.
From a profitability standpoint, the rates charged by financial institutions on traditional loans can represent a substantial expense for farm operators that primarily use debt to fund their operations, much like many other businesses. Interest rate increases are typically used by central banks as a tool to help temper rising inflation, and inflation also causes the cost of key inputs for farming operations (such as fertilizer, seeds, fuel, and equipment) to rise. Combined, an increase in borrowing rates coupled with elevated input costs can put significant pressure on farm profitability. However, as inflationary pressure also affects the market prices for key food commodities, some of that input cost pressure can be offset by increases in farm revenues and incomes.
Interest Rates and Farmland Values
Given the relationship between inflation and interest rates, and farmland’s demonstrated inflation-hedging characteristics, Bonnefield’s investment thesis is that in times of high inflation, Canadian farmland values perform strongly. Historically, farm incomes have increased during inflationary periods and strong farm incomes lead to rising farmland prices.
When valuing farmland, one of the most widely accepted approaches to establishing property values is to divide the rental income that can be generated by a property by a discount rate, which is based on an adjusted “risk-free” interest rate (often a Government of Canada bond yield or, more recently, the Canadian Overnight Repo Rate Average, “CORRA”). This equation, referred to as the capitalization method of valuation, effectively assesses the present value of potential future income generated by a property. Interest rates are a central part of the valuation equation and a higher discount rate (denominator) with no change to the rental income component would decrease the resulting value.
With that said, farm incomes are the single strongest direct drivers of farmland values, and the momentum in market prices for key commodities observed in 2021, and so far in 2022, suggests that incomes will remain healthy in the near-term. Further, while interest rate increases are coming more clearly into view, the overall cost of borrowing is still low compared to historic levels.
Over the years, Bonnefield has observed that when lending is relatively inexpensive and farm incomes are strong, farm operators have been eager to borrow funds to acquire additional land. In 2021, we also saw a high level of transaction activity in the market for Canadian farmland driven by both farmers having ample cash on-hand, as well as pent-up demand after relatively depressed activity in 2020 from the COVID-19 pandemic.
How Could Rising Interest Rates Impact Bonnefield’s Farmland Holdings?
Bonnefield’s core strategy is to invest in a diversified portfolio of prime Canadian farmland on a long-term, fully unlevered basis. We expect that rising interest rates will have a minimal impact on the value of farmland held by our investment partnerships or on the funds’ profitability. Further, as the leading provider of sale leaseback financing to Canadian farmers, Bonnefield’s partnership-based approach to providing an alternative source of capital to the agricultural community has helped many of our farm partners to strengthen their balance sheets by reducing debt. As such, we anticipate that our farmers will weather rising interest rates well. As always, we remain prepared to assist strong Canadian farmers who may have become over-levered by entering into long-term sale leaseback arrangements that allow operators to free up capital, clean up and stabilize their balance sheets, and invest in their businesses.
Having been a trusted partner of farm operators for over 12 years, Bonnefield has seen a number of economic conditions. One thing we know is that farmers are creative and resilient, able to adjust to a wide variety of market conditions in order to maximize the value of their operations. We are confident that this period of inflation and increased interest rates will prove to be no different and Bonnefield is available to support these operators through economic cycles.
About Bonnefield Financial
Bonnefield is the foremost provider of land-lease financing for farmers in Canada. Bonnefield is dedicated to preserving farmland for farming, and the firm partners with growth-oriented farmers to provide farmland leasing solutions to help them grow, reduce debt, and finance retirement and succession. The firm’s investors are individuals and institutional investors who are committed to the long term future of Canadian agriculture. www.bonnefield.com
Contributing Authors:
Andrea Gruza
Managing Partner
Lauren Michell
Senior Principal
Sources:
(1) Reuters News, January 26th, 2022
(2) Bank of Canada, March 2nd, 2022
(3) Statistics Canada, March 16th, 2022
This document is for information purposes only and does not constitute an offer or solicitation to buy or sell any securities in any jurisdiction in which an offer or solicitation is not authorized. Any such offer is made only pursuant to relevant offering documents and subscription agreements. Bonnefield funds (the “Funds”) are currently only open to investors who meet certain eligibility requirements. The Funds will not be approved or disapproved by any securities regulatory authority. Prospective investors should rely solely on the Funds’ offering documents which outline the risk factors in making a decision to invest. No representations or warranties of any kind are intended or should be inferred with respect to the economic return or the tax consequences from an investment in the Funds. The Funds are intended for sophisticated investors who can accept the risks associated with such an investment including a substantial or complete loss of their investment.
